A Comprehensive Guide to Efficient Air Heating and Cooling Systems
Efficient air heating and cooling systems have become a cornerstone of modern residential and commercial comfort. These systems not only maintain indoor temperatures but also improve energy efficiency, reduce utility bills, and contribute to environmental sustainability. In an era where energy costs and climate concerns are growing, investing in advanced heating and cooling technologies is a proactive step for homeowners and businesses alike.
Introduction to Efficient Air Heating and Cooling
As buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption, selecting the right HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) solution plays a critical role in reducing carbon footprints. Whether you’re upgrading an old system or building a new energy-efficient space, understanding the fundamentals and available options is crucial.
Understanding How Efficient HVAC Systems Work
Efficient heating and cooling systems use advanced components such as variable-speed compressors, smart thermostats, and multi-zone control technology to manage indoor climates with precision. Traditional systems often run at full capacity or turn off completely, leading to energy spikes. In contrast, efficient systems modulate performance to maintain consistent comfort with minimal energy waste.
Many of these systems use heat pumps, which transfer heat rather than generating it. This makes them far more energy-efficient than traditional furnaces or electric baseboard heaters. Innovations like inverter technology allow units to adjust their output based on real-time needs, significantly lowering energy use.
Benefits of Using Advanced Heating and Cooling Technology
Energy Savings and Reduced Utility Bills
One of the main benefits of efficient air heating and cooling systems is the dramatic reduction in energy usage. By optimizing power consumption based on actual heating or cooling needs, these systems help homeowners and businesses save on monthly utility expenses. Smart systems can adjust automatically to weather patterns or occupancy schedules, reducing waste.
Improved Comfort and Air Quality
Modern HVAC systems don’t just regulate temperature—they also improve indoor air quality. Many units include built-in air purifiers, dehumidifiers, or HEPA filters that help eliminate dust, allergens, and pathogens. Zoned temperature control also allows different parts of a home or office to be customized to individual comfort levels.
Environmentally Friendly Operation
Energy-efficient HVAC systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions and overall environmental impact. Heat pumps, for example, use electricity far more effectively than combustion-based heating systems. Using a more sustainable system contributes to global energy goals and may qualify users for local green energy incentives.
Real-World Examples of Efficient Heating and Cooling Products
1. Mitsubishi Electric Hyper-Heating H2i® System
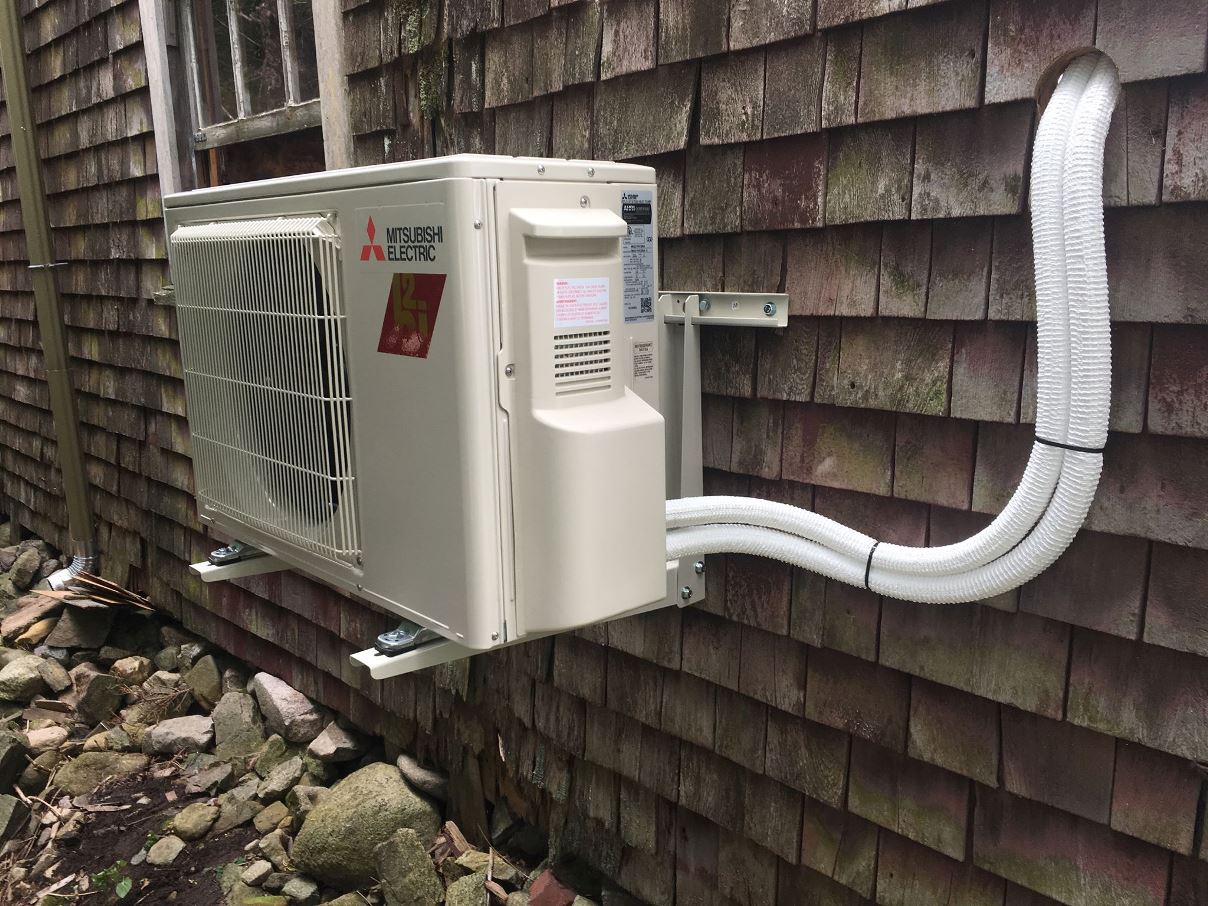

This ductless mini-split system is a top-tier solution for cold climates. Unlike standard heat pumps that lose efficiency in low temperatures, the Hyper-Heating H2i® system maintains high performance even at -13°F (-25°C). Its variable compressor ensures optimal energy use, and individual zones allow occupants to heat or cool specific rooms independently.
Its compact design makes it suitable for older homes without ductwork and newer homes aiming for high-efficiency performance. The system integrates with smart thermostats for app-based controls and scheduling.
2. Lennox SL28XCV Variable-Capacity Air Conditioner

Lennox’s SL28XCV is recognized as one of the most efficient air conditioners available, boasting an impressive SEER rating (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) of up to 28. Its variable-capacity inverter allows it to adjust cooling output in tiny increments, minimizing energy waste.
In practical use, the system maintains consistent temperature levels, reduces humidity, and operates quietly. It’s an excellent solution for homes in warmer climates seeking premium energy savings and comfort.
3. Daikin FIT Heat Pump System
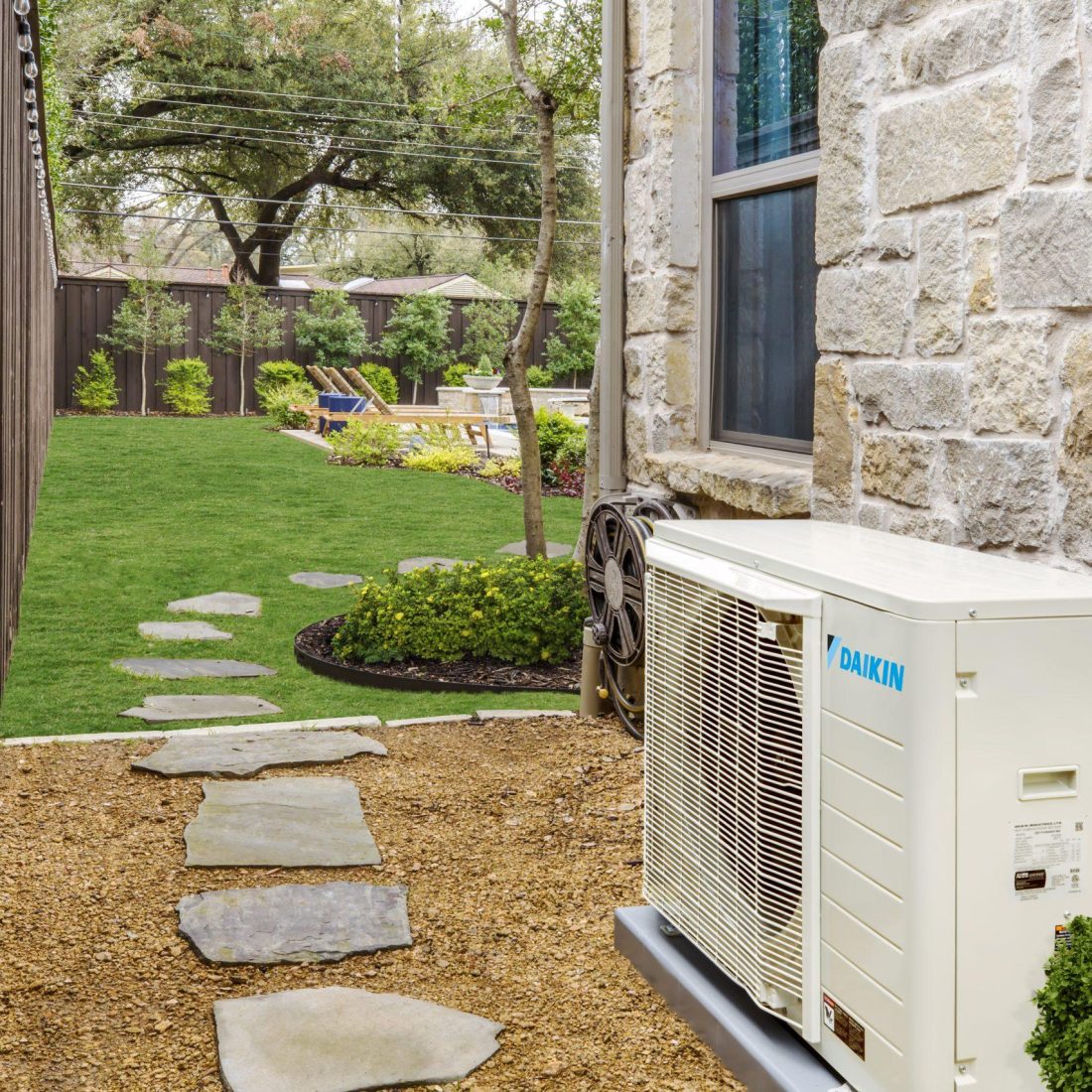

The Daikin FIT system is a compact, side-discharge heat pump that fits into tight spaces and delivers exceptional energy efficiency. It uses inverter technology for precise temperature control, reducing energy use and system wear.
This system is handy for townhouses or urban homes with space constraints. Despite its small size, the Daikin FIT offers reliable performance for both heating and cooling throughout the year.
4. Ecobee Smart Thermostat Premium
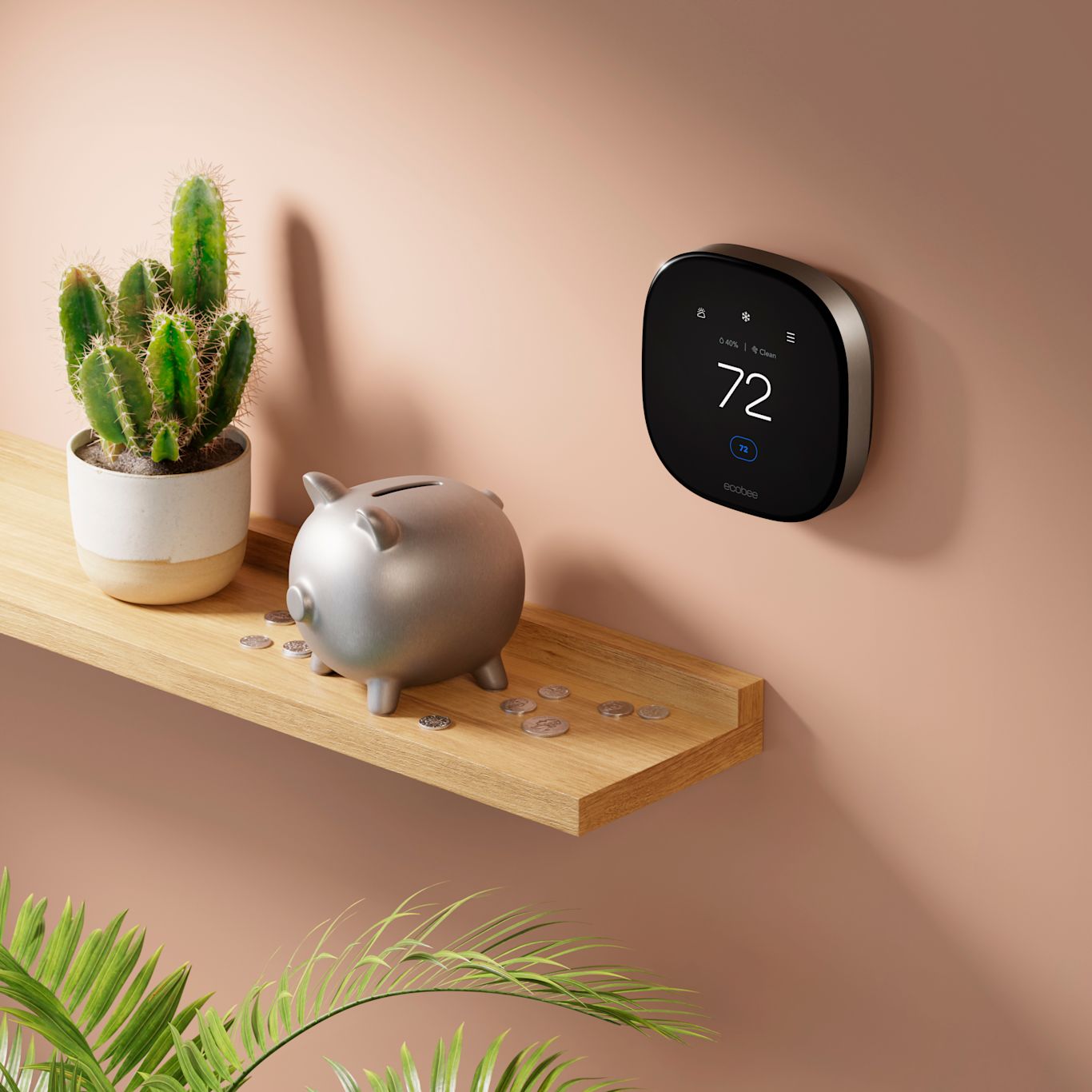

While not an HVAC unit itself, the Ecobee Smart Thermostat enhances the efficiency of heating and cooling systems. It learns user habits, adjusts schedules automatically, and incorporates occupancy sensors and weather forecasting. Paired with a high-efficiency HVAC unit, it significantly cuts down on energy consumption.
The Ecobee is particularly effective in homes where schedules vary daily, as it ensures comfort when needed without wasting energy when rooms are unoccupied.
5. Bosch IDS Premium Inverter Ducted Split System
Bosch’s IDS Premium system combines quiet operation with energy-saving performance. It uses inverter-driven compressors that ramp up or down based on system demand, reducing power usage and maintaining comfort. It’s compatible with most existing ductwork, making it a top choice for retrofits.
This system is ideal for homeowners looking to upgrade from an older furnace or AC unit without a complete overhaul of their ventilation system.
Practical Use Cases and Problem Solving
Retrofitting Old Homes with High Efficiency
Many older homes lack proper insulation or have outdated HVAC systems that waste energy. Modern, efficient systems, especially ductless mini-splits and inverter systems, are ideal for retrofitting. They offer flexibility without requiring invasive remodeling and can be installed room by room to match existing architecture.
Managing Multi-Zone Climate Needs
Families with varying comfort preferences can benefit from multi-zone HVAC systems. Instead of cooling or heating the entire house to one temperature, each room or floor can be set independently. This saves energy and increases satisfaction among occupants.
Climate Adaptation and Energy Efficiency
In regions experiencing extreme weather due to climate change, efficient systems help manage indoor comfort without overloading the grid. Inverter and heat pump technologies work effectively in both scorching heat and frigid winters, adapting automatically to maintain indoor climate balance.
Reducing Noise in Residential Areas
Traditional systems can be noisy, which may disturb sleep or relaxation, especially in urban settings. Efficient systems typically operate at lower decibel levels, making them ideal for bedrooms, apartments, or shared living spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What makes an air heating and cooling system “efficient”?
An efficient system optimizes energy usage through advanced components like variable-speed compressors, inverter technology, and smart thermostats. It uses only the energy needed to maintain comfort, reducing both power bills and environmental impact.
Q2. Can efficient HVAC systems work in older buildings?
Yes, many efficient systems like ductless mini-splits or inverter-based heat pumps are specifically designed for retrofits. They offer flexible installation options and don’t require existing ductwork, making them suitable for older structures.
Q3. How do smart thermostats improve HVAC efficiency?
Smart thermostats learn usage patterns, respond to real-time weather changes, and allow remote control via mobile apps. They help reduce energy consumption by adjusting heating and cooling based on occupancy, scheduling, and outdoor conditions.






