Multi Family Development Companies: A Complete Guide to Modern Housing Solutions
The housing landscape is shifting rapidly, driven by increasing urbanization, demand for affordable living, and smart investment strategies. At the forefront of this evolution are multi-family development companies—firms that plan, design, and build residential complexes with multiple units such as duplexes, townhomes, mid-rise apartments, and high-density communities. These companies are reshaping how people live in cities and suburbs alike, providing scalable housing solutions that serve renters, buyers, and investors.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what multi-family development companies do, how they differ from other real estate firms, the role of technology in their projects, real-world examples of successful developments, and the tangible benefits they deliver to communities and stakeholders.
What Are Multi-Family Development Companies?
Multi-family development companies are real estate developers that specialize in creating residential properties with multiple dwelling units. These can range from small-scale fourplexes to large-scale apartment towers with hundreds of units. These firms manage the entire development lifecycle, from market research and land acquisition to design, construction, leasing, and sometimes ongoing property management.
What sets them apart is their focus on housing density and community-oriented living. Instead of single-family homes on individual plots, these developments provide shared infrastructure, common amenities, and often higher returns on investment per square foot of land.
Core Services Offered by Multi-Family Developers
Most multi-family developers provide a suite of services including architectural planning, zoning, and entitlement processing, environmental review, financial modeling, and general contracting. Some even go a step further with in-house property management or joint venture investment models. Their ability to navigate complex regulations and market demands makes them essential in regions facing housing shortages or urban expansion.
How Technology Is Transforming Multi-Family Development
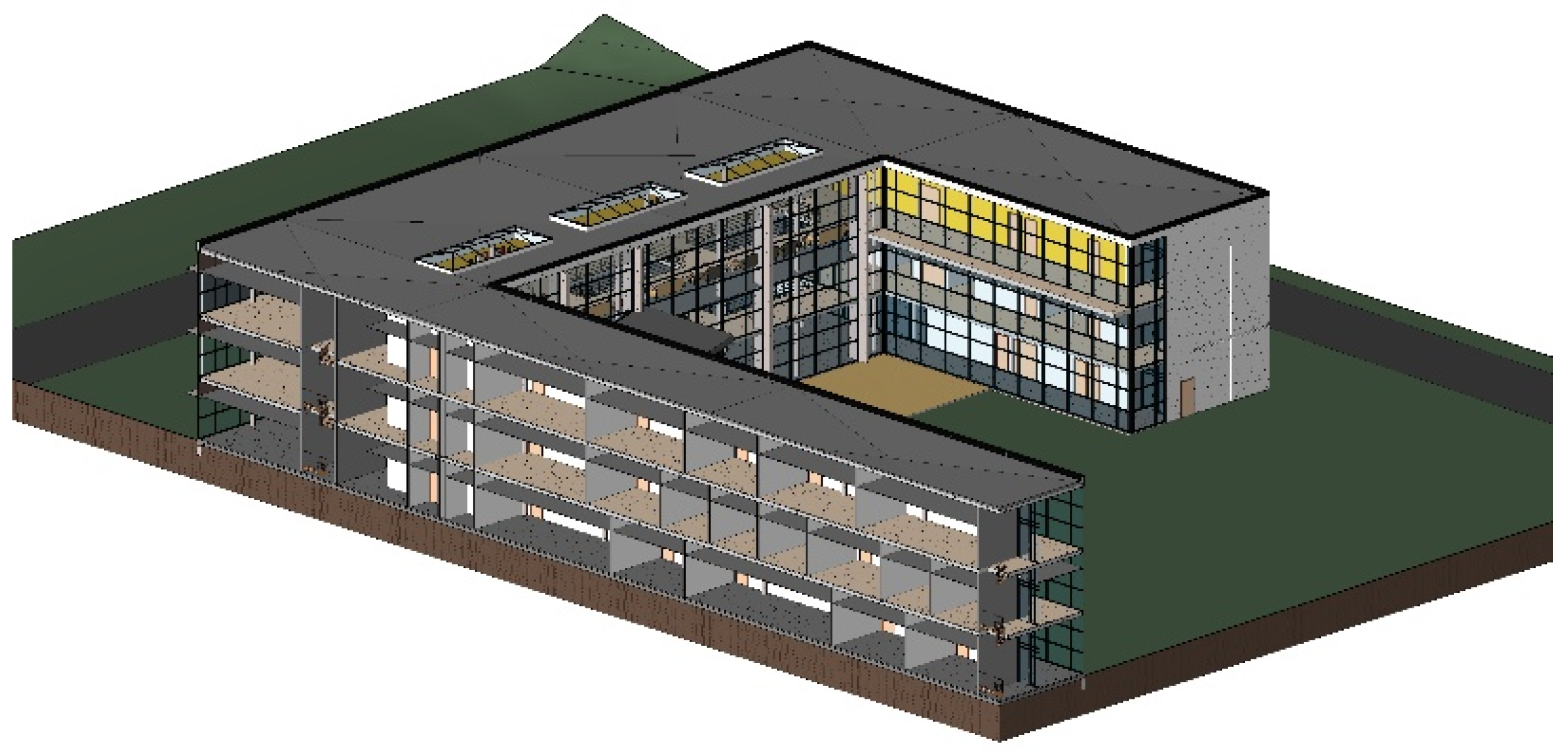
Technology plays a crucial role in the operations and value delivery of multi-family development companies. From design to construction and beyond, innovation enhances efficiency, sustainability, and livability.
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
BIM enables developers to create detailed 3D models that integrate architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) data. This allows for better design coordination, fewer construction errors, and real-time collaboration across teams. Developers can also simulate energy usage, sunlight exposure, and emergency egress paths before breaking ground.
Smart Building Integration
Multi-family buildings increasingly come equipped with smart technologies such as IoT sensors, smart thermostats, keyless entry systems, and centralized building management platforms. These features not only attract tenants but also allow developers to monitor performance, lower maintenance costs, and improve energy efficiency.
Prefabrication and Modular Construction
Some developers are adopting modular construction methods, where units are prefabricated off-site and assembled on location. This reduces construction time, minimizes material waste, and ensures consistent quality. It also allows faster scaling in markets with urgent housing demands.
Real-World Examples of Multi-Family Development Companies and Their Projects
These real-world examples demonstrate how different multi-family development companies execute impactful, scalable housing projects across the U.S.
1. Greystar – Urban High-Rise Development
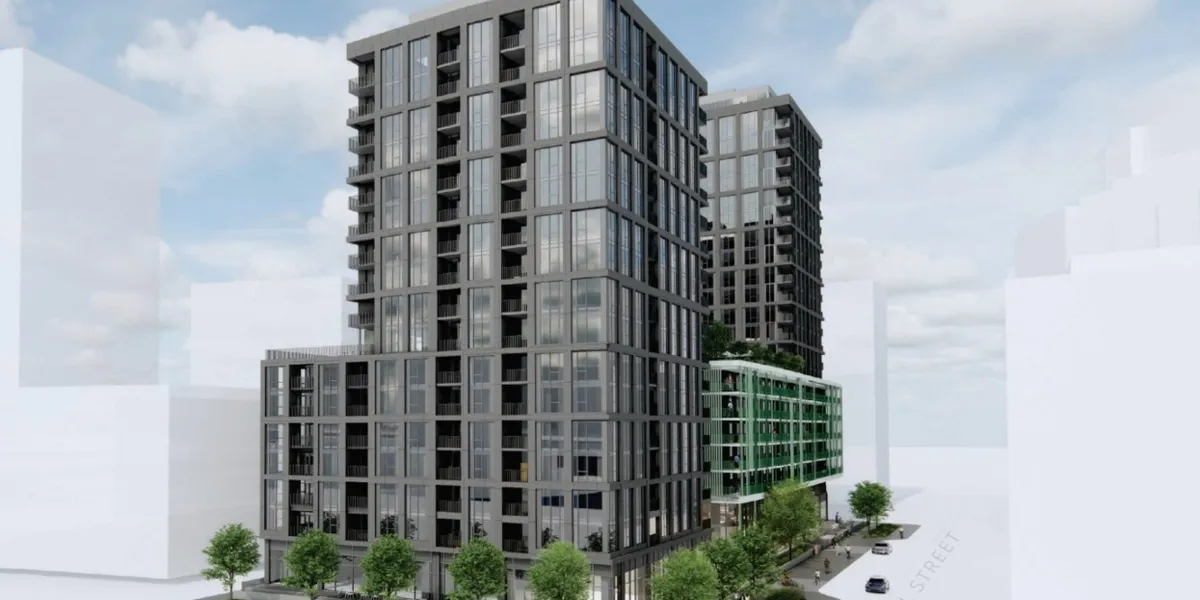

Greystar is one of the world’s largest developers of rental housing. In downtown Seattle, Greystar developed a 40-story mixed-use tower with 450 rental units, retail spaces on the ground floor, and rooftop community amenities. The project included sustainable features like green roofs, water-efficient landscaping, and solar readiness.
Relevance: Greystar showcases how large firms can meet high-density housing needs in tight urban spaces with mixed-use functionality.
2. The NRP Group – Affordable Multi-Family Communities
Based in Ohio, The NRP Group specializes in affordable housing developments. One notable project involved building a 200-unit complex in San Antonio, combining Low-Income Housing Tax Credits (LIHTC) with modern design and community programming. Their developments focus on livability and long-term value.
Relevance: This highlights how multi-family developers address affordability and quality simultaneously, filling crucial market gaps.
3. AvalonBay Communities – Transit-Oriented Developments
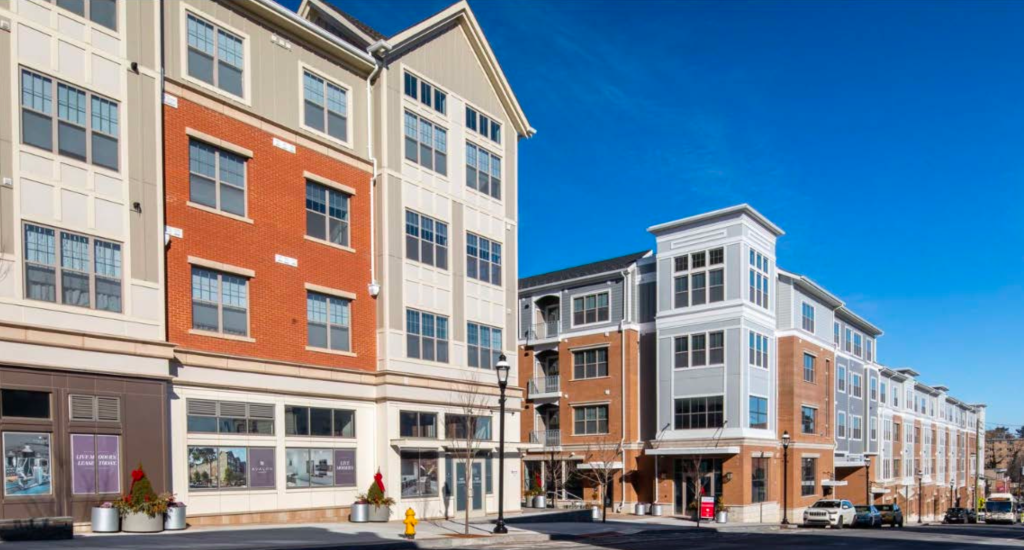

AvalonBay’s projects often target suburban and city-adjacent locations near public transportation. One such development in New Jersey features 300+ luxury apartments with EV charging, bike storage, and proximity to train lines—ideal for commuters.
Relevance: Demonstrates how strategic placement near transportation hubs increases accessibility and sustainability.
4. Trammell Crow Residential – High-End Apartments in Growth Markets
Trammell Crow Residential focuses on upscale rental properties in fast-growing cities like Austin, Charlotte, and Nashville. Their developments often include resort-style pools, co-working lounges, and pet-friendly features. One recent build in Raleigh included a smart home package in every unit.
Relevance: Shows how developers are blending technology and lifestyle amenities to attract millennial renters and professionals.
5. Dominium – Senior-Focused Multi-Family Housing
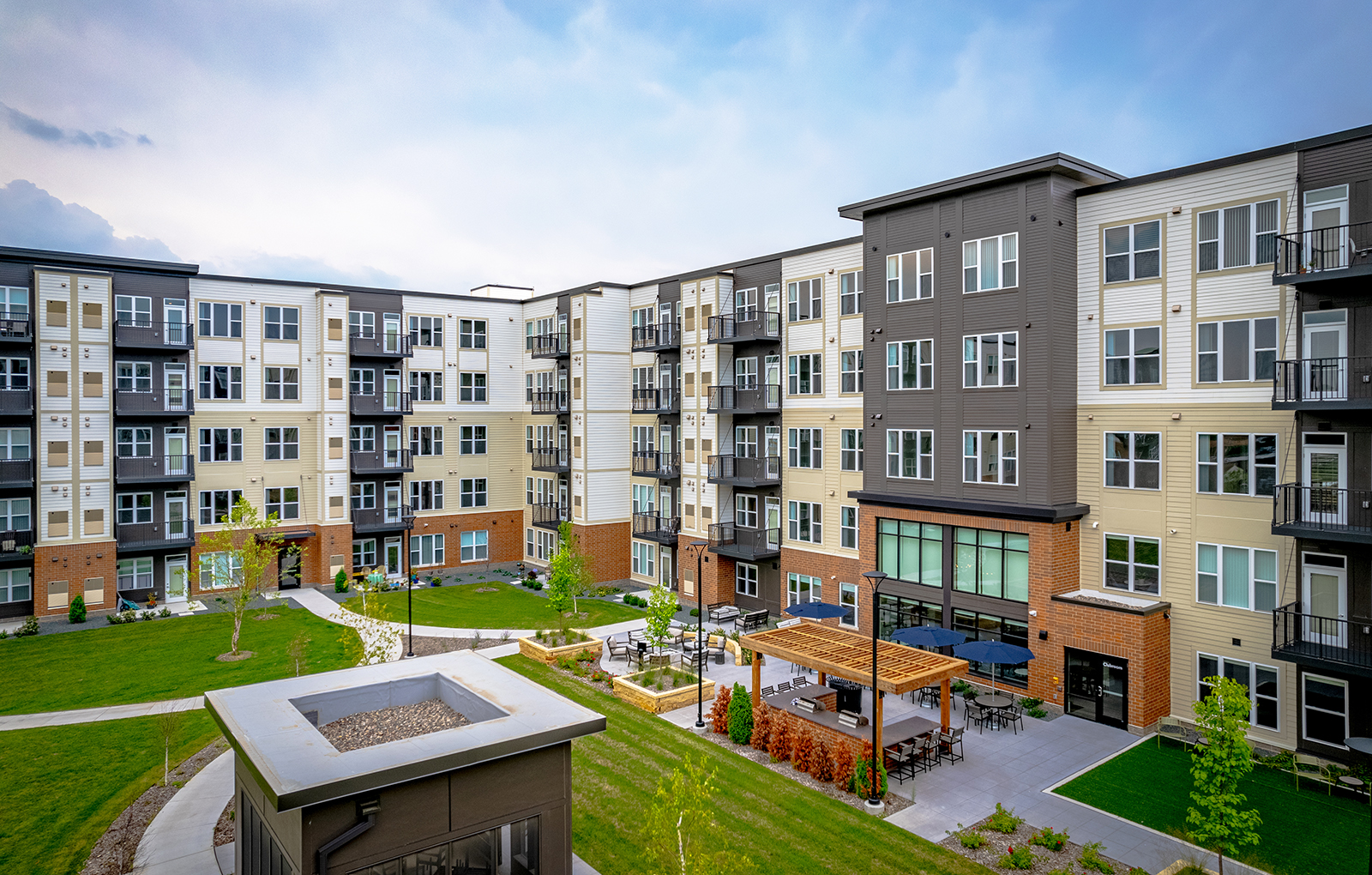

Dominium is a leading developer in senior and workforce housing. In Minnesota, they developed a 150-unit senior apartment community with age-appropriate design, wellness programming, and onsite healthcare partnerships. The project was funded through a public-private collaboration model.
Relevance: Highlights how multi-family developers address demographic-specific needs with thoughtful design and services.
Benefits of Working with Multi-Family Development Companies
Multi-family development companies offer advantages not only to investors and tenants, but also to municipalities, neighborhoods, and the environment.
Efficient Use of Land and Infrastructure
By increasing the number of housing units per parcel, these developments help reduce urban sprawl. Shared utilities, common areas, and compact layouts allow cities to better utilize transportation, sewer, and emergency services.
This density-focused approach supports walkability, reduced vehicle reliance, and healthier urban ecosystems.
Housing Diversity and Affordability
Multi-family developers build a range of units—studios, one-bedroom, two-bedroom, and family-sized apartments—allowing for mixed-income communities. By leveraging incentives like tax credits or zoning bonuses, they can also deliver below-market-rate housing without sacrificing design or safety.
Economic and Job Impact
These projects create local employment during construction and permanent jobs in leasing, property management, and maintenance. They also bring foot traffic to nearby businesses, boosting local economies.
Many developers also partner with local vendors and workforce programs to keep investment within the community.
Customization and Amenity-Rich Living
Modern multi-family projects offer amenities such as rooftop lounges, fitness centers, co-working spaces, and dog parks. Residents enjoy hotel-like perks in a residential environment. Developers also tailor amenities to suit tenant demographics and market demand.
Use Cases Where Multi-Family Development Companies Offer Solutions
Understanding how these companies address real-world housing problems helps illustrate their broad social and economic value.
Use Case 1: Addressing Housing Shortages in Growing Cities
As urban populations surge, cities like Phoenix, Denver, and Orlando face critical housing shortages. Multi-family developers quickly mobilize to build high-volume projects that meet demand faster than traditional builders, helping to stabilize rental prices and alleviate pressure on the housing market.
Use Case 2: Supporting Workforce and Essential Housing
Healthcare workers, teachers, and first responders often struggle to find housing near their jobs. Developers working with public-private partnerships can offer affordable housing for this demographic, keeping essential workers in the communities they serve.
Use Case 3: Revitalizing Underutilized Land
Abandoned lots, aging malls, or brownfield sites are often converted into vibrant housing communities by experienced developers. These redevelopment efforts breathe new life into neglected areas, increasing property values and safety.
Use Case 4: Enabling Smart Urban Growth
Transit-oriented and mixed-use developments reduce traffic congestion and promote environmental sustainability. By placing multi-family units near train stations, shopping districts, and office hubs, developers help cities grow responsibly.
Use Case 5: Providing Senior and Assisted Living Housing
Aging populations need safe, accessible, and socially enriching environments. Developers create age-specific multi-family housing that supports health, independence, and community, reducing the strain on public healthcare systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What dmulti-familyly development company do?
These companies plan, fund, build, and sometimes manage residential housing projects with multiple units. They handle everything from land acquisition and zoning to construction, leasing strategy, and post-completion services.
Q2. Are multi-family developments only for renters?
No. While many projects are built for rental, multi-family developments offer condominiums or co-ops for purchase. Developers may also build townhomes or stacked flats, depending on zoning and market strategy.
Q3. Do multi-family developers work with government programs?
Yes. Many collaborate with city and state programs to access funding through Low-Income Housing Tax Credits (LIHTC), Opportunity Zones, or density bonuses in exchange for offering affordable housing or public amenities.